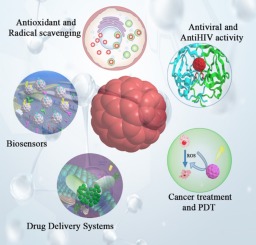
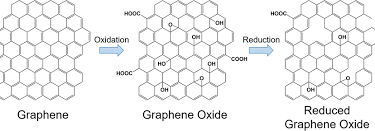
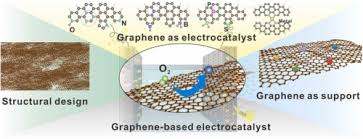
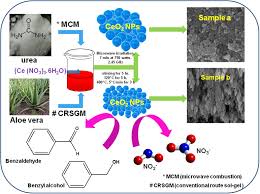
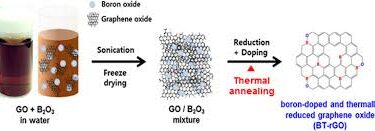
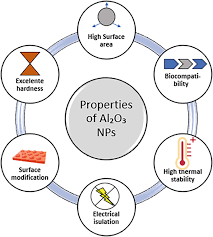
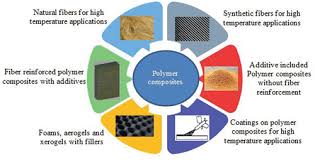
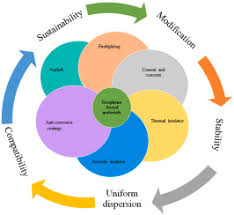
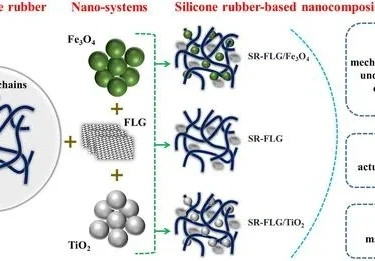
4 Best Applications of Fullerenes in The Biomedical Industry
4 Best Applications of Fullerenes in the Biomedical Industry Introduction Fullerenes, a unique family of carbon molecules characterized by their spherical, ellipsoidal, or tubular shapes, have garnered significant attention in recent decades for their potential applications across various fields, particularly in biomedicine. Discovered in 1985 by researchers Harold Kroto, Robert Curl, and Richard Smalley, fullerenes—commonly