Explained: Graphene, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide and Applications
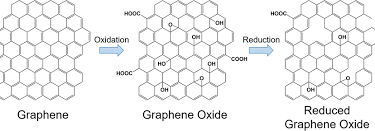
Explained: Graphene, Graphene Oxide, and Reduced Graphene Oxide and Their Applications Introduction In the world of advanced materials, graphene, graphene oxide (GO), and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) have emerged as highly promising substances with a wide range of applications. These materials are distinct forms of graphene, a two-dimensional (2D) carbon nanomaterial that has garnered significant