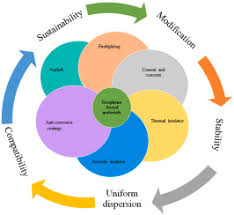
Application Areas of Graphene Paste
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a two-dimensional lattice, is renowned for its extraordinary mechanical, electrical, and thermal properties. The advent of graphene paste, a versatile form of graphene that can be applied like a thick ink or coating, has expanded its range of applications significantly. Below is an overview of various application areas where graphene paste is making an impact.
1. Electronics and Sensors
- Flexible Electronics: Graphene paste can be used to create conductive inks for flexible, stretchable, and lightweight electronic devices. This is particularly useful in wearable electronics, such as smart clothing, health-monitoring patches, and flexible displays.
- Printed Circuits: Graphene paste serves as an ideal material for printing flexible circuits directly onto substrates using low-cost, scalable printing technologies, such as inkjet and screen printing. This application is vital for the development of flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) and smart electronics.
- Sensors: The high conductivity and surface area of graphene make it a promising material for sensors. Graphene paste is applied in the production of gas, chemical, and biosensors, where it can detect minute changes in environmental conditions. It is particularly effective in applications like environmental monitoring and healthcare diagnostics.
2. Energy Storage and Batteries
- Supercapacitors: Graphene paste can be used to enhance the performance of supercapacitors by improving charge storage and conductivity. It allows for the fabrication of electrodes that can store large amounts of energy, leading to faster charging times and longer cycle lifespans.
- Lithium-ion and Other Batteries: Incorporating graphene paste into the electrodes of lithium-ion or sodium-ion batteries enhances their charge/discharge cycles, capacity, and overall efficiency. Graphene’s conductive properties allow for better electron flow and faster charging.
- Flexible Energy Devices: The flexibility and conductivity of graphene paste enable the development of bendable batteries and energy storage devices, which is crucial for flexible and wearable electronics.
3. Thermal Management
- Heat Dissipation: Graphene’s high thermal conductivity makes it an excellent material for thermal management. Graphene paste can be applied to surfaces that need to dissipate heat efficiently, such as in electronics, LEDs, and power devices. It helps prevent overheating by distributing heat more evenly across components.
- Thermal Coatings: Graphene-based thermal pastes and coatings are increasingly used to improve the thermal performance of various products, ranging from computers to automotive systems.
4. Composite Materials
- Lightweight, High-Strength Composites: Graphene paste can be incorporated into polymers, metals, and ceramics to create high-performance composites. These materials are used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and construction, offering enhanced strength, durability, and resistance to wear while maintaining a lightweight profile.
- Conductive Composites: By adding graphene paste to composites, manufacturers can create materials that are both strong and conductive. These materials are essential in applications like electromagnetic shielding, anti-static coatings, and conductive adhesives.
5. Coatings and Protective Films
- Anti-Corrosion Coatings: Graphene paste is used to create protective coatings for metals, preventing corrosion and enhancing the longevity of machinery, pipelines, and other metal structures exposed to harsh environments.
- Water-Repellent Coatings: Graphene’s hydrophobic properties make it ideal for use in water-repellent coatings. These coatings are applied to surfaces such as textiles, electronics, and building materials, providing resistance against water and moisture.
- Self-Healing Coatings: In some advanced applications, graphene-based coatings can offer self-healing properties, where the material can repair minor damages or scratches when exposed to heat or other stimuli.
6. Biomedical and Healthcare Applications
- Drug Delivery Systems: Graphene paste can be functionalized to carry and deliver drugs to specific areas in the body. Its large surface area and biocompatibility allow it to serve as a carrier for controlled drug release, improving the effectiveness and precision of treatments.
- Biosensors: In addition to general sensors, graphene paste is used in the development of highly sensitive biosensors for detecting specific biomarkers, such as those in cancer diagnostics or other medical tests. Its electrical properties enable accurate detection of bioanalytes at low concentrations.
- Wound Healing: Graphene paste is being investigated for its use in wound healing applications, where it can be applied as a dressing to promote faster tissue regeneration and act as a bactericidal agent.
7. Environmental Applications
- Water Purification: Graphene-based materials, including paste, are being explored for their use in water filtration systems. The paste can be used to create membranes that filter out nanoparticles, heavy metals, and other contaminants, providing a low-cost, efficient solution for water purification.
- Pollution Control: Graphene paste can be used to create materials that absorb or neutralize air and water pollutants. It can be used in applications like air filtration systems or to remove harmful chemicals from industrial effluents.
8. Smart Fabrics and Textiles
- Conductive Textiles: Graphene paste can be integrated into fabrics to create smart textiles that are conductive and interactive. These textiles can be used in wearable technology, such as shirts that monitor vital signs or clothing that adjusts its properties based on environmental conditions.
- Thermal Regulation: Graphene-enhanced textiles can offer smart thermal regulation, helping to maintain body temperature by adapting to heat and cold. This has promising applications in sportswear and outdoor clothing.
9. Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
- Graphene-infused Filaments: Graphene paste can be used as a filament in 3D printing, allowing for the creation of stronger, more conductive, and thermally efficient parts. It opens up new possibilities for manufacturing complex parts with enhanced performance characteristics.
- Rapid Prototyping: The ability to print graphene-based materials enables rapid prototyping of electronic devices, sensors, and structural components with advanced properties, accelerating product development cycles.
10. Energy Harvesting and Conversion
- Solar Cells: Graphene paste can be applied in the fabrication of flexible, lightweight, and high-efficiency organic solar cells. Graphene enhances the conductivity of the electrodes, leading to better electron transport and more efficient energy conversion.
- Thermoelectric Generators: Graphene-based materials are being investigated for use in thermoelectric generators, where they could help convert waste heat into electrical energy in applications ranging from industrial processes to wearable devices.
Conclusion
Graphene paste is a revolutionary material that harnesses the unique properties of graphene in a convenient, versatile form. Its applications span numerous industries, from electronics and energy storage to healthcare, environmental protection, and advanced manufacturing. As research continues, the potential uses of graphene paste are likely to expand even further, offering innovative solutions to some of the most pressing challenges of modern technology and industry.
