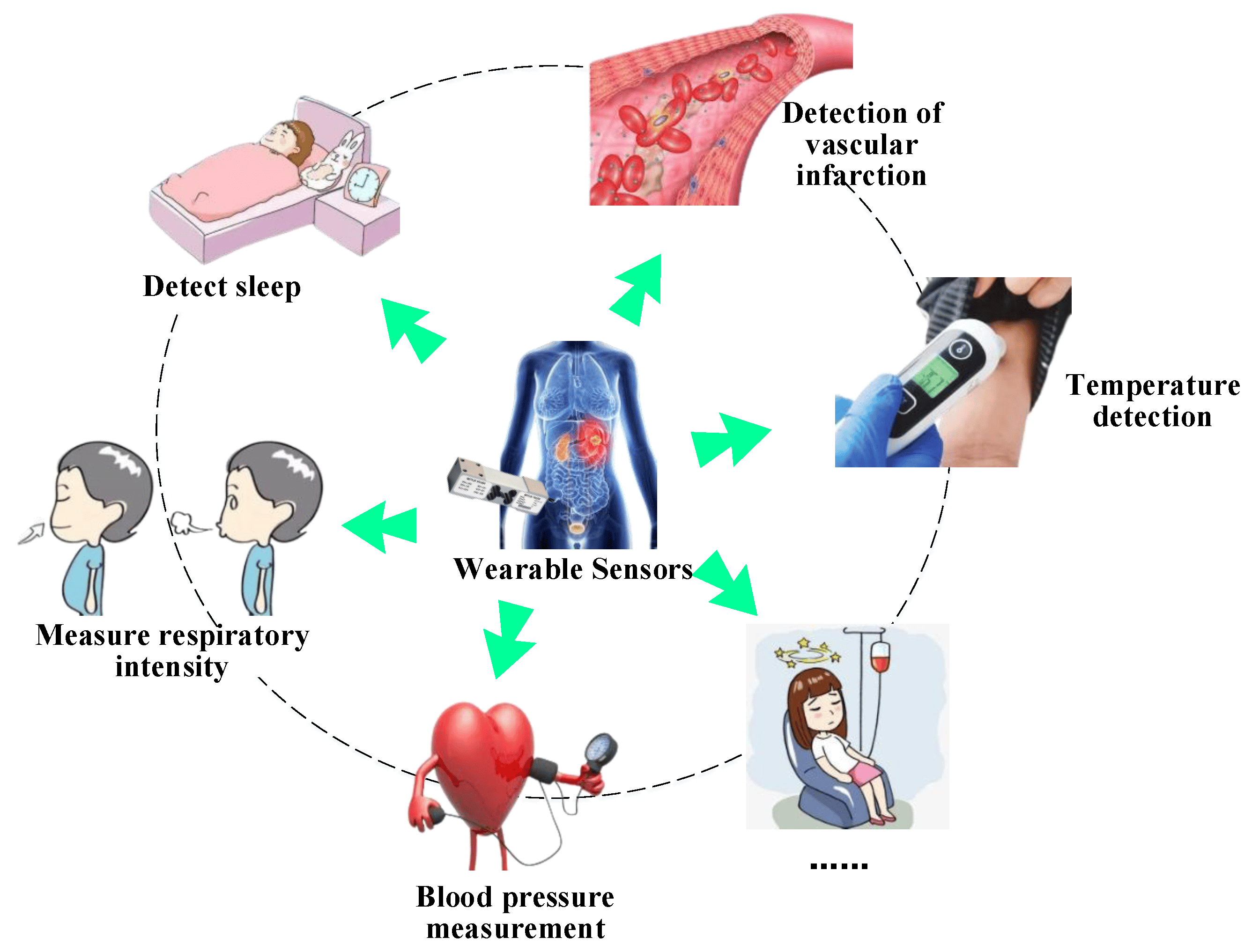
Nanosensors to Understand Vital Metrics of People: Advancing Personalized Health Monitoring
Nanosensors, an innovative class of devices designed at the nanoscale, are revolutionizing the way we monitor and understand human health. These miniature sensors can detect and measure vital metrics with unparalleled precision, providing real-time insights into physiological conditions. From chronic disease management to fitness tracking, nanosensors are paving the way for a new era of personalized health monitoring.
What Are Nanosensors?
Nanosensors are devices that leverage nanotechnology to detect and analyze biological, chemical, or physical signals at the molecular level. By operating at the nanoscale, these sensors can interact with cells, molecules, and tissues, enabling highly sensitive and specific measurements.
Key Features of Nanosensors for Vital Metrics
- High Sensitivity:
- Capable of detecting minute changes in physiological parameters such as glucose levels, heart rate, and oxygen saturation.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- Provides continuous data for immediate insights and timely interventions.
- Miniaturization:
- Compact and lightweight, ideal for wearable and implantable devices.
- Specificity:
- Designed to target specific biomarkers for accurate diagnostics.
- Integration with IoT:
- Connects with smartphones and cloud systems for data analysis and remote monitoring.
Applications of Nanosensors in Health Monitoring
- Chronic Disease Management:
- Tracks conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases, providing actionable data for patients and clinicians.
- Wearable Fitness Devices:
- Measures metrics such as heart rate, hydration levels, and calorie expenditure to support fitness goals.
- Implantable Sensors:
- Monitors critical health parameters from within the body, such as blood glucose or intracranial pressure.
- Early Disease Detection:
- Identifies biomarkers for conditions like cancer, enabling early diagnosis and treatment.
- Drug Delivery and Monitoring:
- Ensures precise delivery of medications and tracks their effects in real-time.
- Neuro Monitoring:
- Measures brain activity and neurotransmitter levels, aiding in the management of neurological disorders.
Advantages of Using Nanosensors
- Precision and Accuracy:
- Delivers highly accurate measurements, reducing diagnostic errors.
- Non-Invasive Options:
- Many nanosensors can operate through wearable or skin-adhered devices, minimizing discomfort.
- Early Intervention:
- Detects anomalies at an early stage, improving outcomes for chronic and acute conditions.
- Personalized Healthcare:
- Tailors monitoring and treatment plans to individual needs based on real-time data.
- Improved Patient Engagement:
- Provides patients with actionable insights, promoting proactive health management.
Challenges in Deploying Nanosensors
- Cost of Development:
- High production costs can limit accessibility for mass adoption.
- Data Security and Privacy:
- Handling sensitive health data requires robust cybersecurity measures.
- Scalability:
- Scaling up manufacturing while maintaining quality and precision is a challenge.
- Regulatory Approvals:
- Meeting stringent regulatory standards for medical devices can be time-consuming.
- Integration with Existing Systems:
- Ensuring compatibility with current healthcare infrastructure and technologies.
Future Directions
- AI and Machine Learning:
- Integrating AI for predictive analytics and better interpretation of nanosensor data.
- Energy Efficiency:
- Developing energy-efficient nanosensors to extend battery life in wearable devices.
- Multi-Functionality:
- Creating nanosensors capable of monitoring multiple parameters simultaneously.
- Eco-Friendly Manufacturing:
- Employing sustainable methods and materials for production.
- Global Accessibility:
- Focusing on cost-effective designs to make nanosensors accessible in low-resource settings.
Conclusion
Nanosensors are redefining the landscape of health monitoring, offering unprecedented precision and personalization. By overcoming current challenges and integrating with advanced technologies, nanosensors hold the potential to revolutionize healthcare, enabling earlier interventions, better disease management, and improved patient outcomes. As research and development progress, nanosensors are poised to become a cornerstone of the future of personalized medicine.
