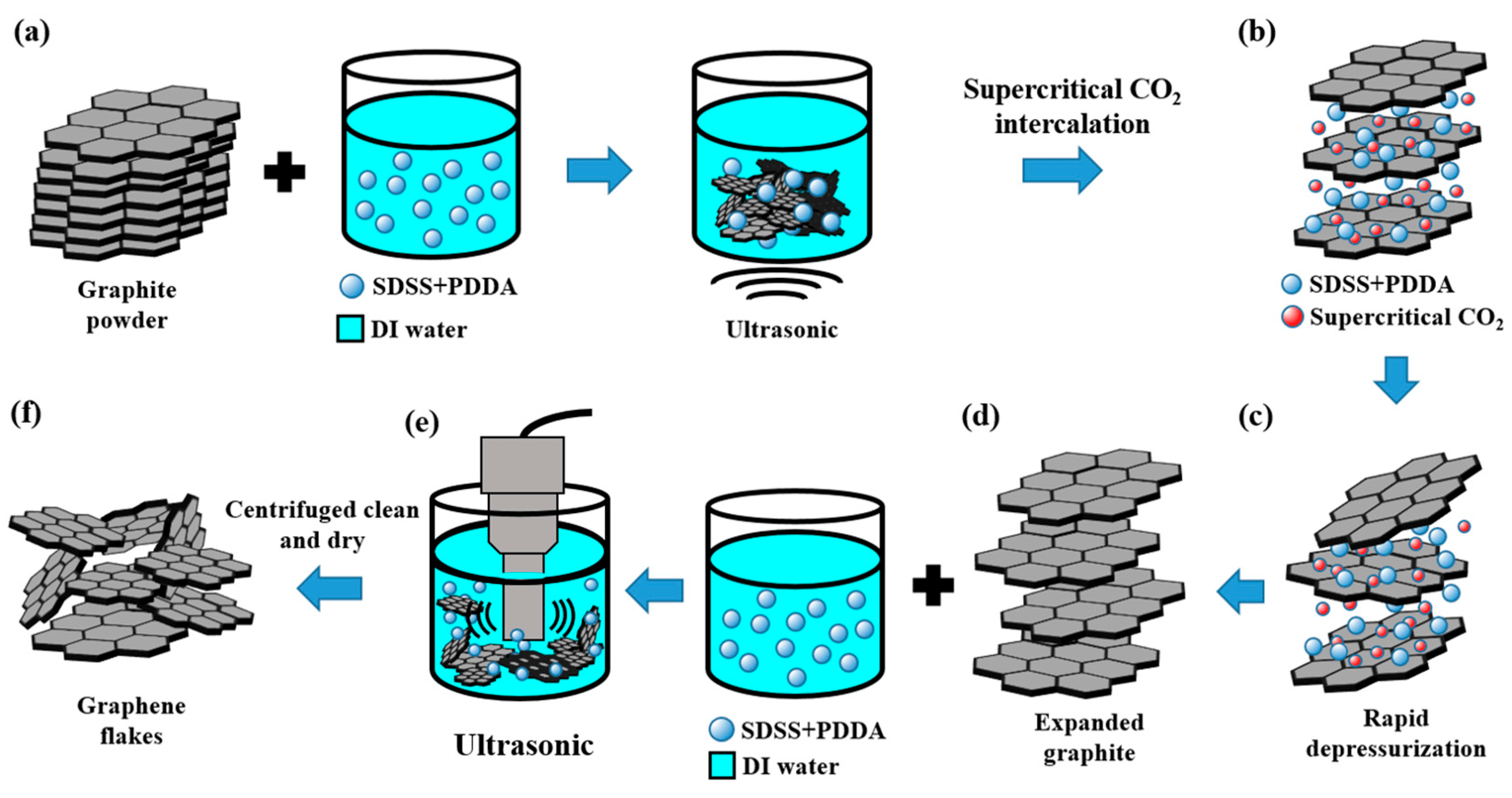
Graphene’s Potential as a High-Performance Surfactant
Graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, has garnered significant attention for its extraordinary properties, such as high electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and thermal conductivity. Beyond its use in electronics and materials science, graphene is now being explored for its potential as a high-performance surfactant in various industrial applications. This article delves into the role of graphene as a surfactant, its benefits, applications, and the challenges faced in harnessing its full potential.
What Are Surfactants?
Surfactants, or surface-active agents, are compounds that lower the surface tension between two substances, such as liquid and gas, liquid and liquid, or liquid and solid. They are commonly used in cleaning products, emulsifiers, and dispersants. Surfactants play a vital role in stabilizing suspensions, reducing foaming, and enhancing solubility in various systems.
Traditional surfactants are often based on organic compounds, which can have limitations in terms of stability, environmental impact, and effectiveness in certain applications. As industries seek more sustainable and efficient alternatives, graphene emerges as a promising candidate due to its unique properties.
Graphene’s Structure and Unique Properties
Graphene’s two-dimensional structure gives it a high surface area and the ability to interact with other materials in innovative ways. Some of its key properties include:
- High surface area: A single layer of graphene has a surface area of around 2630 m²/g.
- Hydrophobicity: Graphene’s structure can naturally repel water, making it suitable for use in water-repelling applications.
- High mechanical strength: Graphene is stronger than steel, allowing it to maintain its integrity even in harsh conditions.
- Electrical conductivity: Graphene is an excellent conductor of electricity, making it useful in applications requiring electrical stability.
- Flexibility and adaptability: Graphene’s ability to form composites and structures allows for customization in surfactant applications.
Graphene as a Surfactant: How It Works
Graphene can act as a surfactant due to its amphiphilic nature, meaning it can interact with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic substances. This unique feature makes it highly effective in reducing the surface tension between different phases, including water-oil, oil-water, or solid-liquid interfaces.
Graphene oxide (GO), a derivative of graphene, is particularly effective as a surfactant because it contains oxygenated functional groups on its surface, such as hydroxyl, carboxyl, and epoxide groups. These functional groups enhance the dispersibility of graphene in water and other solvents, making it easier to create stable colloidal dispersions or emulsions.
The ability of graphene oxide to interact with both water and oil phases enables it to function as a stabilizing agent in emulsions, dispersing and stabilizing particles within liquids. The charge on graphene oxide also contributes to its ability to stabilize suspensions by preventing particles from aggregating.
Benefits of Graphene as a Surfactant
1. Improved Stability
Graphene’s high surface area and functional groups allow for better stabilization of emulsions and suspensions compared to traditional surfactants. It can prevent phase separation in oil-water mixtures and stabilize particles in colloidal suspensions, enhancing the longevity and effectiveness of the system.
2. Environmental Friendliness
Graphene oxide, as a surfactant, is potentially more environmentally friendly than many conventional surfactants, which can be toxic or non-biodegradable. Graphene-based surfactants are water-soluble and can be used in aqueous environments, which makes them less harmful to the environment.
3. Enhanced Dispersion of Nanoparticles
In industries like nanotechnology, the ability to disperse nanoparticles in solvents is crucial. Graphene’s surfactant properties can help stabilize nanoparticles in solution, prevent agglomeration, and ensure uniform dispersion. This is particularly valuable in nanocomposite production, where high-performance materials are created by embedding nanoparticles in a matrix.
4. Non-toxic and Biocompatible
Graphene oxide can be engineered to be biocompatible and non-toxic, making it suitable for use in biomedical applications such as drug delivery systems, biosensors, and wound healing. Traditional surfactants in biomedical applications can sometimes cause adverse reactions, but graphene oxide presents a safer alternative.
5. Cost-Effective and Versatile
Graphene can be produced through various methods, including chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and chemical reduction of graphene oxide, making it relatively cost-effective for industrial applications. Its versatility also allows it to be used in a wide range of products, from cosmetics and pharmaceuticals to lubricants and cleaning agents.
Applications of Graphene as a Surfactant
1. Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
Graphene oxide has been shown to be effective in skin care products such as creams, lotions, and shampoos. As a surfactant, it helps disperse active ingredients in water-based formulations and stabilizes emulsions. It also provides anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, making it valuable in anti-aging and skin rejuvenation products.
2. Oil Spill Remediation
Graphene’s ability to interact with both hydrophobic and hydrophilic substances makes it an excellent candidate for use in oil spill cleanup. Graphene-based surfactants can help disperse oil in water, improving the effectiveness of oil spill dispersants and potentially making the cleanup process more efficient.
3. Drug Delivery Systems
In pharmaceutical applications, graphene oxide can serve as a surfactant to stabilize drug molecules, ensuring they remain in solution and are efficiently delivered to targeted areas in the body. This could lead to more effective treatments, particularly in targeted drug delivery for cancer therapies.
4. Food and Beverage Industry
Graphene-based surfactants could revolutionize the food industry, where they can be used to stabilize emulsions in food products such as dressings, sauces, and beverages. The ability to improve stability and texture could enhance the quality of food products while ensuring safety and bio-compatibility.
5. Water Treatment and Environmental Remediation
Graphene-based surfactants can be utilized in water purification systems to remove pollutants or oil contaminants from water bodies. They can aid in the emulsification and removal of hazardous materials, contributing to cleaner water and a healthier environment.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While graphene shows great promise as a surfactant, there are challenges to overcome, such as the scalability of production, cost, and potential environmental impacts associated with large-scale production. Additionally, the long-term stability of graphene oxide in various formulations needs to be further studied to ensure that it retains its properties over time.
However, the potential of graphene as a surfactant in various industries is immense. As production techniques improve and sustainability concerns drive the demand for more environmentally friendly alternatives, graphene-based surfactants are likely to become a prominent solution in many sectors.
Conclusion
Graphene’s unique properties make it an exciting candidate for use as a high-performance surfactant in a wide range of applications. From cosmetics and biomedicine to oil spill remediation and food processing, graphene’s ability to stabilize emulsions, disperse nanoparticles, and improve overall system performance opens up new possibilities for industries looking for more sustainable and effective solutions. With ongoing research and development, graphene-based surfactants may well become a game-changer in the coming years.