The Best Way to Utilize Carbon Nanotubes in Industry with Potential Applications
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) have emerged as one of the most versatile nanomaterials, offering unique properties that make them invaluable across a range of industries. From their exceptional mechanical strength to their electrical conductivity, CNTs hold immense potential for innovation and efficiency improvements in various fields.
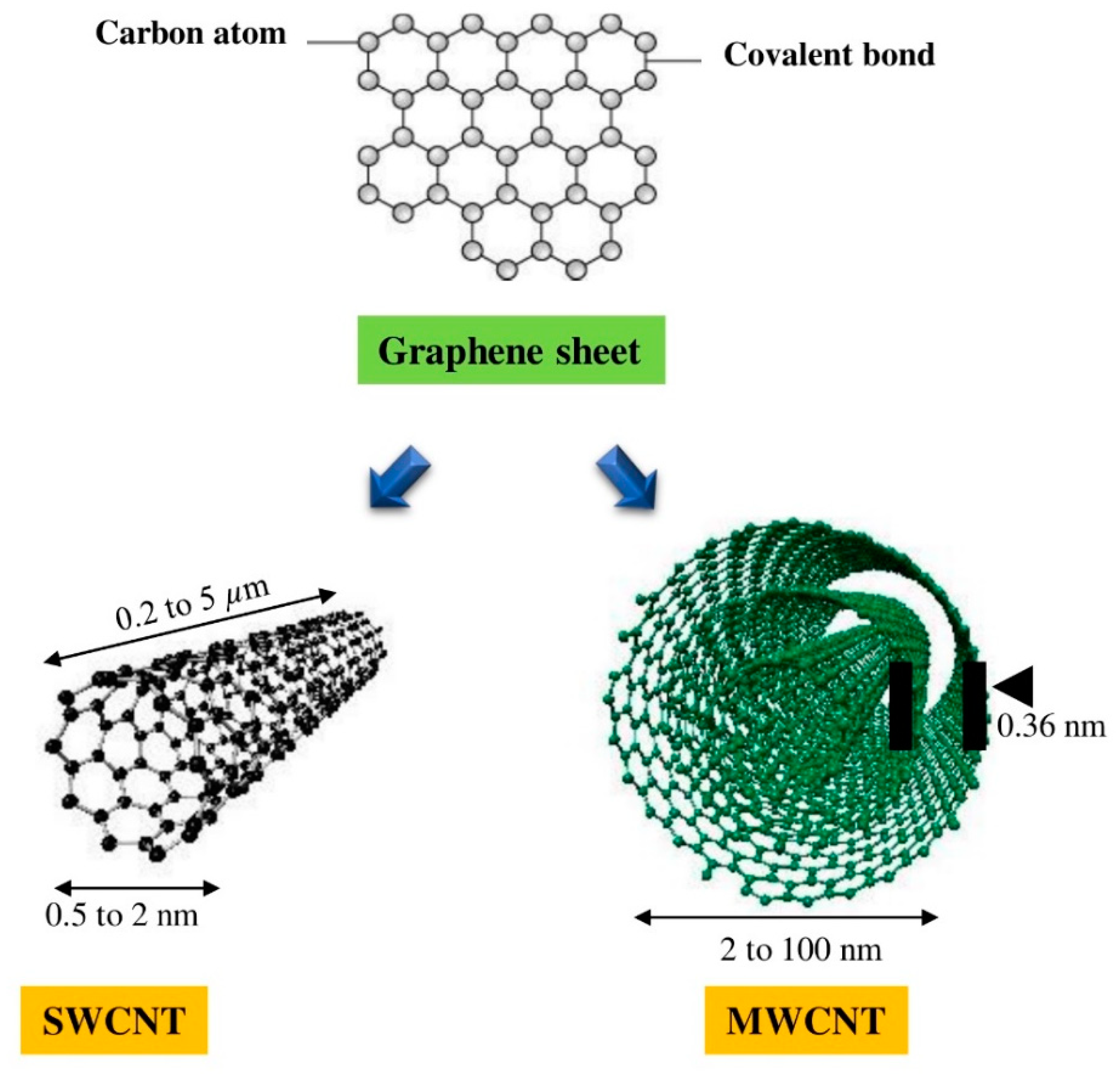
Properties of Carbon Nanotubes
- Exceptional Strength:
- CNTs have a tensile strength up to 100 times greater than steel, making them ideal for lightweight and durable materials.
- Electrical Conductivity:
- CNTs can function as excellent conductors or semiconductors, depending on their structure.
- Thermal Conductivity:
- They possess high thermal conductivity, making them suitable for heat dissipation applications.
- Flexibility:
- CNTs are lightweight and can be woven into flexible materials.
- Chemical Stability:
- Their resistance to chemical degradation ensures longevity in harsh environments.
Industrial Applications of Carbon Nanotubes
- Electronics and Semiconductors:
- CNTs are being used to develop smaller, faster, and more energy-efficient transistors.
- They are integrated into flexible and wearable electronics for advanced consumer devices.
- Energy Storage:
- In batteries and supercapacitors, CNTs enhance energy density, charge rates, and lifespan.
- CNTs are also being explored for hydrogen storage in fuel cell technology.
- Composite Materials:
- Adding CNTs to polymers and metals creates lightweight, high-strength composites used in aerospace, automotive, and sports equipment.
- Thermal Management:
- CNTs are incorporated into thermal interface materials (TIMs) for effective heat dissipation in electronics and LED lighting systems.
- Medical Applications:
- CNTs are employed in drug delivery systems and biosensors due to their biocompatibility and ability to penetrate cells.
- Water Purification:
- CNT-based membranes offer high efficiency in filtering contaminants from water due to their nanoscale pores.
- Textiles:
- Smart textiles integrated with CNTs provide advanced functionalities like conductivity, energy storage, and temperature regulation.
Future Potential and Research Directions
- Renewable Energy:
- CNTs can improve the efficiency of solar cells by enhancing charge transport and light absorption.
- Research is underway to integrate CNTs into wind turbines for lighter and more durable blades.
- Environmental Applications:
- CNTs are being studied for use in air purification and carbon capture technologies.
- Quantum Computing:
- CNTs’ quantum properties are opening possibilities in developing components for quantum computers.
- 3D Printing:
- CNTs can be incorporated into advanced 3D printing materials, enabling stronger and more functional printed components.
Challenges in Utilizing Carbon Nanotubes
- Scalability:
- Producing high-quality CNTs on a large scale remains a challenge.
- Cost:
- The high cost of CNT production limits their accessibility for certain applications.
- Health and Safety:
- Ensuring safe handling and mitigating potential health risks from CNT exposure is critical.
- Standardization:
- The lack of industry-wide standards for CNT properties and applications hinders widespread adoption.
Conclusion
Carbon Nanotubes are poised to revolutionize multiple industries with their unique properties and versatile applications. While challenges like cost and scalability remain, ongoing research and innovation are steadily addressing these hurdles. By harnessing the potential of CNTs, industries can achieve breakthroughs in efficiency, performance, and sustainability, paving the way for a transformative future.
