Nanotechnology Applications in Daily Life
Nanotechnology, the science of manipulating matter at the molecular or atomic scale (typically at dimensions of 1 to 100 nanometers), has rapidly advanced in recent years. Its applications are becoming increasingly pervasive across a variety of industries, impacting everything from healthcare to energy efficiency. While nanotechnology may seem like something confined to futuristic science fiction, it is already playing a significant role in our daily lives. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most prominent nanotechnology applications in daily life, highlighting how it has improved the quality, efficiency, and sustainability of everyday products and services.
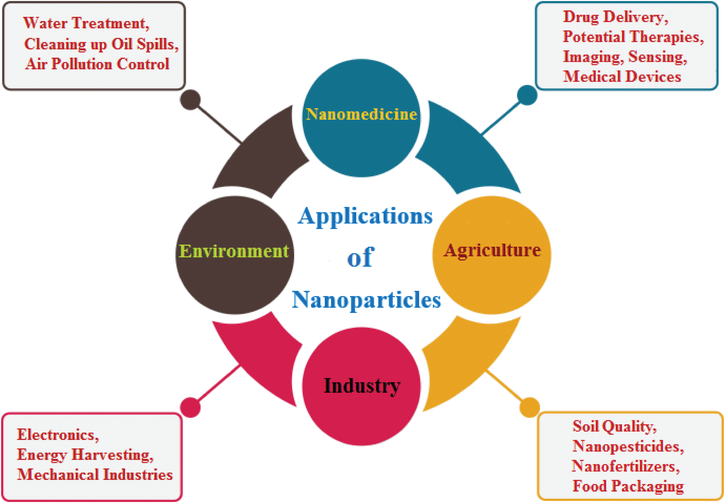
1. Nanotechnology in Healthcare
a. Drug Delivery Systems
Nanotechnology has revolutionized the way drugs are delivered to patients. Nanoparticles can be engineered to carry drugs directly to targeted areas in the body, such as cancerous cells, thus minimizing side effects and maximizing therapeutic effectiveness. Liposomes, nanospheres, and nanocapsules are common forms of nanocarriers that allow drugs to be delivered more precisely and efficiently. This has the potential to enhance treatments for various conditions, including cancer, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
b. Diagnostic Tools
Nanotechnology is also being used to improve medical diagnostics. Nanosensors and nanodevices can detect diseases at an early stage with remarkable accuracy. For instance, nanoparticles can help detect biomarkers associated with cancer, heart disease, or infections, allowing for earlier, more effective treatments. Nanoparticles in biosensors are also used in diagnostic tests for pregnancy, HIV, and diabetes, providing fast and reliable results.
c. Wound Healing and Tissue Engineering
Nanomaterials such as silver nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes are used in wound dressings to accelerate the healing process. Their antimicrobial properties help prevent infection, while their structural properties promote faster tissue regeneration. In the field of tissue engineering, nanofibers and hydrogels are used to create scaffolds for cell growth, aiding the regeneration of damaged tissues and organs.
2. Nanotechnology in Electronics
a. Smart Devices
The miniaturization of electronic devices is largely attributed to nanotechnology. Advances in semiconductor technology have made it possible to create smaller, faster, and more efficient electronic components, which have contributed to the development of smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearables. Quantum dots, nanowires, and carbon nanotubes are playing an essential role in enhancing the performance and energy efficiency of these devices.
b. Touchscreens and Displays
Nanotechnology has enabled the development of advanced touchscreen technologies and OLED (organic light-emitting diode) displays, which offer brighter, more energy-efficient screens for smartphones, TVs, and other devices. Nanocoatings are applied to enhance the durability of touchscreens, making them resistant to scratches, fingerprints, and water.
c. Data Storage and Memory
The ability to store and process vast amounts of data has significantly increased with the help of nanotechnology. Nanomaterials like magnetic nanoparticles are used in data storage devices such as hard drives and solid-state drives (SSDs) to increase their storage capacity and speed. Additionally, research into quantum computing—which leverages the principles of quantum mechanics at the nanoscale—could soon lead to breakthroughs in computing power and memory storage.
3. Nanotechnology in Food and Agriculture
a. Food Packaging
Nanotechnology is being used to develop innovative food packaging materials that extend the shelf life of products. Nanocomposites, such as those made with nanoclays or silver nanoparticles, are incorporated into packaging materials to enhance their barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, and light. These advancements help preserve food for longer periods while maintaining its nutritional value and reducing waste.
b. Food Safety and Quality Control
Nanosensors are used to detect foodborne pathogens, toxins, and contaminants, ensuring food safety. Nano-based sensors can also help monitor the quality of food products in real-time, alerting consumers or producers to potential spoilage or degradation. For example, nanosensors embedded in packaging can detect the presence of harmful bacteria like E. coli or Salmonella.
c. Precision Agriculture
Nanotechnology is transforming the way we grow and manage crops through precision agriculture. Nano-fertilizers and nano-pesticides are more efficient than traditional versions, as they deliver nutrients or pesticides directly to plants at the nanoscale. This results in reduced chemical use, less environmental pollution, and increased crop yields. Additionally, nano-sensors can monitor soil conditions, water content, and plant health, providing farmers with more accurate and timely data.
4. Nanotechnology in Environmental Protection
a. Water Purification
One of the most promising applications of nanotechnology in environmental protection is in the field of water purification. Nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes, graphene oxide, and silver nanoparticles are used to filter contaminants from water, including heavy metals, bacteria, and viruses. Nanofilters can be more effective and energy-efficient than traditional filtration systems, making them ideal for both industrial and residential water treatment.
b. Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy
Nanotechnology has significantly advanced the field of energy by improving the efficiency of both conventional and renewable energy sources. Nanomaterials are used in solar cells to increase their light absorption and energy conversion efficiency. For example, quantum dots and nanostructured coatings are being used to create more efficient photovoltaic cells. Nanotechnology is also improving the efficiency of batteries and supercapacitors used in electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
c. Environmental Remediation
Nanotechnology can be used to clean up environmental contaminants through a process known as nanoremediation. Nanoparticles, particularly iron-based nanoparticles, are used to break down hazardous substances like oil spills, pesticides, and industrial chemicals in soil, water, and air. Their high surface area and reactivity make them effective at neutralizing pollutants.
5. Nanotechnology in Personal Care and Cosmetics
a. Sunscreens and Skincare
Nanotechnology has improved the effectiveness and appearance of many personal care products, especially in sunscreens and skincare products. Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles are commonly used in sunscreens to provide broad-spectrum protection without leaving a white, greasy residue on the skin. These nanoparticles are transparent, allowing for better absorption and a more aesthetically pleasing product.
b. Anti-Aging Products
In the cosmetics industry, nanotechnology is used to create products that deliver active ingredients deeper into the skin. Nanoencapsulation allows for controlled release of ingredients like vitamins, antioxidants, and peptides, which are absorbed more efficiently by the skin. This has led to the development of anti-aging and skin rejuvenation products with improved performance.
c. Hair Care
In hair care, nanotechnology has been employed to create more effective shampoos, conditioners, and styling products. Nanoparticles of silica, keratin, and other compounds are used to improve hair strength, shine, and manageability, while also protecting hair from environmental damage.
6. Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its many benefits, nanotechnology still faces several challenges. Safety concerns regarding the potential toxicity of nanomaterials, particularly when they enter the body or the environment, need to be addressed. Comprehensive studies are still required to understand the long-term effects of exposure to nanoparticles.
Additionally, costs associated with the synthesis of nanomaterials and the scalability of production can be limiting factors. As research advances and more efficient production methods are developed, these barriers may be overcome.
7. Conclusion
Nanotechnology has already begun to enhance our daily lives in ways that were once unimaginable. From medical breakthroughs and advanced electronics to food safety, environmental protection, and cosmetics, the applications of nanotechnology continue to grow. As innovation progresses, nanotechnology will undoubtedly lead to even more efficient, sustainable, and effective solutions, further shaping the future of many industries and improving the quality of life for people around the world.
By harnessing the potential of nanotechnology, we are not only solving current problems but also laying the groundwork for the future of healthcare, energy, agriculture, and environmental sustainability. As these applications expand, they promise to offer even greater benefits, making nanotechnology an indispensable part of modern life.