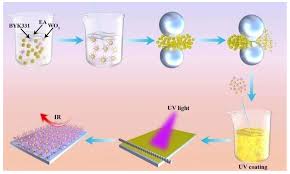
Nano Coatings: The Ultimate Barrier for UV and NIR Radiation
Introduction
In today’s world, the need for enhanced protection against various environmental factors is growing across industries, particularly with the increasing concerns surrounding ultraviolet (UV) and near-infrared (NIR) radiation. These types of radiation can damage materials, degrade products, and have negative effects on human health. Fortunately, nano coatings have emerged as a cutting-edge solution to address these challenges, offering superior protection against UV and NIR radiation, thus improving the durability and longevity of materials. In this article, we explore how nano coatings are revolutionizing the protection of products, surfaces, and even human health by blocking harmful radiation.
1. Understanding UV and NIR Radiation
A. Ultraviolet Radiation (UV)
UV radiation, which lies between 100 and 400 nm in wavelength, is divided into three categories:
- UVA (320-400 nm): The least energetic but most abundant UV radiation that penetrates deeply into the skin, contributing to premature aging and an increased risk of skin cancer.
- UVB (280-320 nm): More energetic and responsible for sunburns and skin damage. It can also contribute to DNA mutations, leading to cancer.
- UVC (100-280 nm): The most harmful UV radiation, but fortunately, it is absorbed by the Earth’s ozone layer.
Long-term exposure to UV radiation causes material degradation, discoloration, and weakening of polymeric and organic materials, making UV protection essential in many applications, such as sunscreens, automotive coatings, and electronics.
B. Near-Infrared Radiation (NIR)
NIR radiation lies just beyond the visible spectrum, from approximately 700 nm to 2500 nm. While less energetic than UV radiation, NIR can penetrate deep into materials, causing thermal damage and energy loss. In the context of buildings, vehicles, and even wearable technologies, NIR protection is necessary to prevent overheating and to improve energy efficiency by reducing the absorption of heat.
2. Nano Coatings: A Revolutionary Solution
Nano coatings are ultra-thin layers of materials that are engineered at the nanoscale (ranging from 1 to 100 nanometers). These coatings can be designed to enhance the properties of the surface they cover, offering a range of benefits including UV and NIR radiation protection, anti-corrosion, self-cleaning, scratch resistance, and improved durability. The remarkable capabilities of nano coatings stem from their ability to manipulate materials at the atomic level, enabling the creation of coatings that exhibit unique optical, chemical, and mechanical properties.
3. Mechanisms of UV and NIR Radiation Blocking in Nano Coatings
A. UV Radiation Protection
The effectiveness of nano coatings in blocking UV radiation lies in the material composition and structural design of the coating. These coatings can work through two primary mechanisms:
- Absorption: Certain nanomaterials, such as titanium dioxide (TiO2), zinc oxide (ZnO), and cerium oxide (CeO2), are highly effective at absorbing UV radiation. When applied as nano coatings, these materials absorb harmful UV rays and convert them into heat energy, preventing them from penetrating deeper into the material or surface.
- Reflection and Scattering: Nano coatings can also reflect and scatter UV radiation by incorporating materials like silica nanoparticles or ceramic nanoparticles. The nano-sized particles in the coating help reflect UV light away from the surface, preventing the radiation from reaching the underlying material or substrate.
B. NIR Radiation Protection
NIR radiation is a form of infrared light that carries heat, and excessive absorption can lead to overheating and degradation of materials. Nano coatings designed for NIR protection typically use materials that are specifically tailored to absorb or reflect heat.
- Thermal Insulation: Some nano coatings utilize materials such as carbon-based nanoparticles (e.g., carbon nanotubes or graphene) to block NIR radiation and prevent thermal buildup. These coatings can reflect infrared radiation away from the surface, minimizing heat absorption and keeping surfaces cooler.
- Heat Dissipation: Nanomaterials with high thermal conductivity can help dissipate absorbed heat, preventing temperature increases in sensitive equipment or structures. For example, metal nanoparticles or ceramic-based nanomaterials can spread out the heat energy over a larger area, reducing localized heating effects.
4. Applications of Nano Coatings for UV and NIR Radiation Protection
Nano coatings are becoming indispensable in a wide range of industries where exposure to UV and NIR radiation is a concern. Some of the most common applications include:
A. Solar Panel Protection
Solar panels are directly exposed to UV and NIR radiation, which can degrade their performance over time. By applying nano coatings that block UV and NIR radiation, manufacturers can extend the lifespan of solar panels and improve their efficiency by preventing heat buildup.
B. Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, nano coatings are used on vehicle surfaces to protect them from UV and NIR radiation. UV-protective coatings prevent fading and degradation of paint, while NIR coatings reduce the heat absorbed by vehicle interiors, improving comfort and reducing the need for air conditioning.
C. Electronics and Displays
Electronics, including smartphones, tablets, and televisions, are often exposed to UV radiation from sunlight. Nano coatings can be applied to screens to prevent UV-induced damage and to improve durability. Additionally, NIR-blocking coatings can help protect electronic components from heat buildup, enhancing the longevity and performance of devices.
D. Clothing and Textiles
In the fashion and textile industry, nano coatings are used to make clothing and outdoor fabrics more resistant to UV radiation. These coatings can be incorporated into sunscreen fabrics, helping to block harmful rays from reaching the skin. NIR-resistant textiles are also being developed for use in sportswear and protective clothing.
E. Building Materials
Building materials such as windows, facades, and roofing can benefit from nano coatings that offer UV and NIR protection. These coatings not only reduce heat absorption and prevent UV-induced degradation but also help maintain the energy efficiency of buildings by reflecting infrared radiation and reducing the need for cooling systems.
5. Benefits of Nano Coatings for UV and NIR Protection
The adoption of nano coatings to combat UV and NIR radiation offers a host of benefits:
- Improved Durability: Nano coatings protect surfaces and materials from UV-induced degradation, preventing fading, cracking, and brittleness, and ultimately prolonging the lifespan of products.
- Enhanced Comfort: In applications such as vehicles and clothing, nano coatings that reduce heat absorption from NIR radiation can significantly improve comfort by keeping surfaces cooler.
- Energy Efficiency: By reducing the heat absorbed from NIR radiation, nano coatings can contribute to energy savings in both buildings and vehicles, reducing the need for air conditioning and cooling.
- Environmental Protection: Nano coatings help protect not only the materials underneath but also the environment, as they reduce the need for replacement materials and prevent the degradation of natural resources.
- Cost-Effective: Over time, nano coatings can be a cost-effective solution by reducing the need for frequent replacements and enhancing the durability of products.
6. Challenges and Future Outlook
Despite the tremendous advantages of nano coatings, some challenges remain:
- Scalability: Producing nano coatings on a large scale while maintaining consistency and quality can be challenging.
- Environmental and Health Concerns: The impact of nanoparticles on the environment and human health needs to be thoroughly evaluated to ensure the safe use of these materials in commercial products.
Looking forward, continued research into new nanomaterials and coating techniques is expected to address these challenges and enable even more effective and sustainable solutions for UV and NIR radiation protection.
Conclusion
Nano coatings are revolutionizing the way we protect products and surfaces from the damaging effects of UV and NIR radiation. With their superior protective properties, nano coatings are not only enhancing the durability and performance of materials but are also driving forward advancements in energy efficiency, comfort, and environmental sustainability. As nanotechnology continues to evolve, these coatings will likely become even more advanced, enabling new possibilities in fields ranging from solar energy to automotive design, electronics, and textile engineering.
